FAQ
I have forgotten my username and password
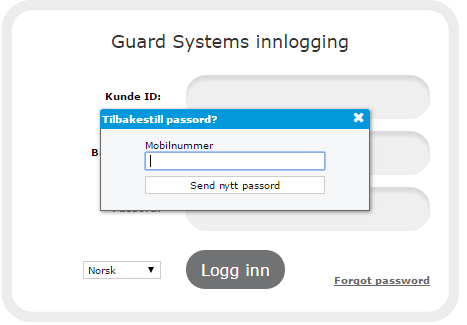
“If your phone number is registered to you as a user, you can get new information as below.
1. go to: login.guardsystems.com
2. Select “Forgotten password”
3. Enter your phone number (you should write your countrycode, for example +46 702 12 34 56) and then press “Send new password”.

You will receive an SMS with all the details.
After logging in, you will be asked for the new password you wish to use.
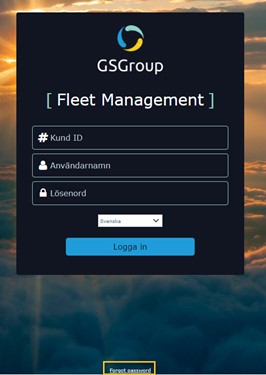
Log in: Fleet Management
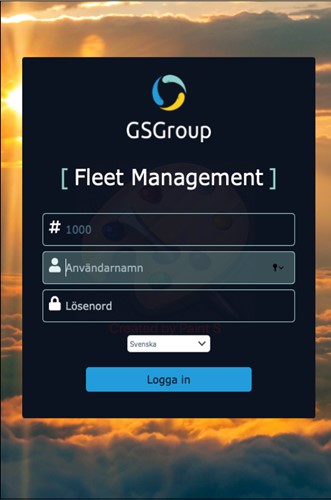 Login via mobile/tablet:
Download our App:“GSGroup Asset Manager” from the App Store or Google Play.
Login via mobile/tablet:
Download our App:“GSGroup Asset Manager” from the App Store or Google Play.


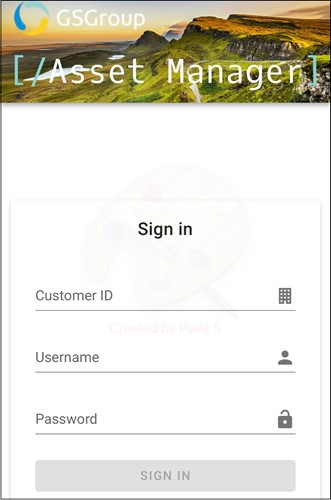 If you do not have this information, you can order login details here
If you do not have this information, you can order login details here
How do I set up a zone registration?
You can easily find the address/location you want by entering the address in the search tool.
Zoom in until you see the area you want to create a zone registration for.
You can click on the padlock to open up so you can move around the map image.
Tips! You can also use the scroll function on the mouse to zoom in or out.
Click on the zone registration tool, see below.
After pressing the zone tool, the button turns blue. Then, when you move the mouse down the map, the mouse pointer becomes a cross. Now you are ready to draw the zone registration.
Click once in the map to start from where you want to start drawing the zone. You will see a blue line when you move the mouse. Click with the mouse on the locations to circle the place where you want to make a zone registration. The area will be gray as you have drawn in. This means you can save the location in the system. You do this by right-clicking and you will be given three choices.
“Undo last point” – “Stop drawing and save” – “Delete the zone”. In this case, we are happy with the location and choose “Stop drawing and save”.
You will now see the following window
Zone name: Here you write a name for the zone
Select Point Editing
Here you choose if you want to have a color on the zone
Alarm when: Here you define the different alarm types you want.
Export ID: Reference number of the zone to another system linked by API.
E-mail: Here you choose who should receive the information about the different events for the current zone
Mobile phone: Here you select the person who will receive the information on the different events for the current zone.
Object: Here you select which objects the zone will apply to.
New items: Check this box if you want new units purchased to have these zones automatically.
Periods: define when the zone should be active
Now you see the zone area you created. You can edit or delete the zone at any time.
What do the different colors under the items mean?
 Ignition on
Ignition on
 Ignition of
Ignition of Unit has not reported for 24 hours
Unit has not reported for 24 hours
Can the GPS unit be connected via the OBDII socket?
In most cases, the OBDII socket can be used for a quick and easy installation. What you should consider is whether the OBDII socket is in a place where you can connect the OBDII cable and that it is not in the way and exposed to unnecessary wear and tear.
Who can help me with the installation? We work with several installers who can help you install your product.
Menu functions
 , you will get information about the page you are currently on.
, you will get information about the page you are currently on.

How do I register Spotguard for the first time?
When registering Spotguard for the first time, you must enter the Spotguard serial number and your customer information in the web form available on the activation page(https://gsgroup.se/form/aktivering-spotguard/).
The Spotguard serial number is on the device.
My device does not appear when I log in
Please contact us on +46 08-550 124 65 or info@gsgroup.se.
Log in: Spotguard tracking device
 Login via mobile/tablet:
Download our App:“GSGroup Spotguard” from the App Store or Google Play.
Login via mobile/tablet:
Download our App:“GSGroup Spotguard” from the App Store or Google Play.

 If you do not have this information, you can order login details here
If you do not have this information, you can order login details here
Is the Spotguard service available internationally?
Guard Systems has trained staff in Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Hungary. Moreover, our partner network extends to the Netherlands, Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Spain, so the service is available in most of Europe. The general conditions apply.
Theft of objects. What do I do?
First, you should report the theft to the police and your insurance company. Once you have received a reference number for the police report, contact GSGroup.
Tel: + 46 08-29 22 90
Why does the tracking device not report?
If the transmitter has no GSM coverage or if the battery is dead, the transmitter will not report its position.
If the transmitter is located indoors, e.g. in a garage, the GSM coverage may be too poor and the transmitter cannot report its position. The location of the transmitter is also important, as poor location means poor coverage. If the transmitter is outdoors without reporting, the battery may be dead. Log in to the system to check this. If the battery voltage is below 3.2 volts, last report, the battery should be replaced.
This can also be checked by opening the transmitter and pressing the “reset button” on the circuit board. A light on the circuit board should start flashing when the transmitter restarts. If no light is flashing, the battery is dead.
If you do not know where the transmitter is located, contact GSGroup support.
Is Spotguard waterproof?
The casing is manufactured according to to the standard of IP class 67. This means it is dust-proof and can withstand being submerged in water for short periods. However, do not mount it under water, as this will affect GPS reception and GSM coverage.
How do I get a map image from my Spotguard device(s)?
By logging in to the Spotguard app or the Guardsystems Fleet system with the details provided by customer service.
Why has my Spotguard not reported anything or reported incorrectly?
Please note that due to the technical limitations of GPS satellite signals and GPRS coverage, we cannot guarantee that the GPS device can transmit its position 100% of the time.
GPS/GPRS coverage may vary in different areas and there may be downtime, outages or radio shadowing.
Also remember that GPS is an outdoor technology. Therefore, GPS accuracy will be difficult to achieve while the device is inside buildings.
Will Spotguard be able to display positions in other countries?
Spotguard will work wherever there is a functioning GPRS network.
The coverage of the telecommunication service is provided by Telenor and Telenor’s roaming partners worldwide.
What are GSM signals?
The Global System for Mobile Communications, GSM, is the most widely used mobile phone system in the world. By using GSM signals from multiple base stations, a rough position can be achieved with a accuracy of a few hundred meters within a city or area. The GSM location is shown as a circle on the map. Spotguard will not necessarily appear in the center of the circle, but somewhere in or around the circle. To minimize power consumption, the GSM method is standard for Spotguard – this helps to extend the life of the battery in Spotguard. Spotguard Plus devices can be set up to use GSM triangulation as the default method of positioning or as a backup for when there is no GPS signal.
What are GPS signals?
Global Positioning System: The GPS system consists of 24 satellites orbiting the Earth. By using GPS radio signals, an exact position of the Spotguard can be achieved, with an accuracy of 1-50 meters to the nearest road, and if possible the nearest street number. The GPS position is shown as a marker on the map.
The device consumes more power when using GPS than it does when using only GSM positioning. It is therefore recommended to use GPS positioning only for short periods to save battery power for as long as possible, for example in situations where you need to locate the device if it has been stolen. Only Spotguard Plus devices have a GPS receiver.
Why does the transmitter show the wrong position?
If the transmitter fails to contact the satellites (GPS), it shows its position via GSM triangulation (an approximate position). If the GSM coverage is poor, the accuracy is reduced. Some areas of the country have poorer GSM coverage. Even a poor placement of the transmitter, or if the transmitter is located indoors, this also results in poorer GSM coverage. The accuracy can vary between 350 meters – 4 mil depending on the distance to the nearest towers.
To find all transmitters in case of theft without GPS or GSM position, radio frequency (RF) is used to locate the position of the transmitter.
How do I know that my transmitter is working?
Log in to the system and check the date when the transmitter reported its last position. If you do not have login details, you can order them via our website:
https://gsgroup.se/form/bestaellning/bestaellning-tillbehoer/
I have forgotten my username and password
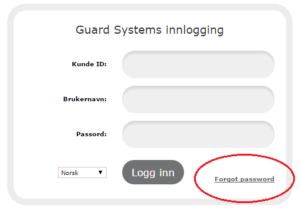 3. Enter your phone number (you should use +46, e.g. +46 702 12 34 56) and then press “Send new password”:
3. Enter your phone number (you should use +46, e.g. +46 702 12 34 56) and then press “Send new password”:
 6. You will receive an SMS with all the details.
7. After logging in, you will be asked for the new password you want.
6. You will receive an SMS with all the details.
7. After logging in, you will be asked for the new password you want.
Log in: Travel log
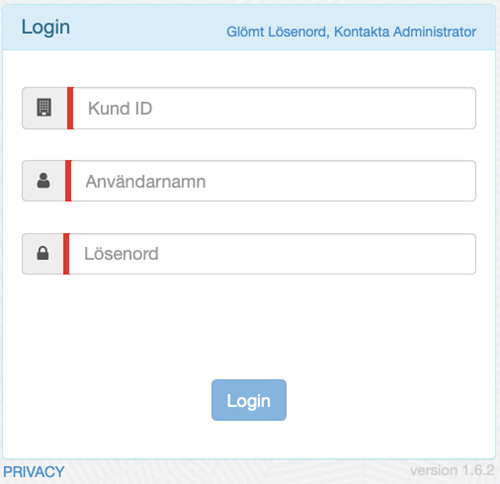 Log in via mobile/tablet:
First download our App:“GSGroup Travellog” from the App Store or Google Play.
Log in via mobile/tablet:
First download our App:“GSGroup Travellog” from the App Store or Google Play.


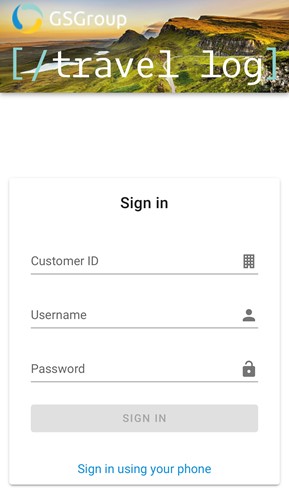 If you do not have these details, you can order login details here
If you do not have these details, you can order login details here
I need more Dallas keys, how do I do?
Orders for Dallas keys must be done in writing by sending an email to support@guardsystems.com.
The order must contain the following information about the users who need a key*:
– Name
– E-mail address
– Mobile number
*Additional information may be required where specified in the contract.
I accidentally merged two trips. What do I do now?
You can easily undo the merger. Combined trips will be marked in the list of your trips with a chain symbol below the start/destination address.
1. Select the “Edit trip” button on the trip you want to split.
2. Select “Split trip” to undo the merge.
3. Travel is now shared
I forgot to identify myself when driving a car, how do I retrieve my trips?
The travel log will detect trips that are missing drivers under the “Missing drivers” menu during trips. This list is available to all drivers within the same department.
1. Select the time period when the trip took place and find the trip in the list.
2. Select the “Change” button to the left of the trip
3. Then select “Select trip” in the next screen
The trip is now linked to you as a driver.
Can I install the devices myself?
The units are relatively easy to install, but require some technical knowledge. Tips and advice can be found in the installation guide included in the package you received. Contact us if you have any questions about the installation.
What is a travel log?
The best way to show that you are not using your employer’s car for private purposes is to keep a travel log, detailing all trips, both private and business. Even if you have a company car, it can be important to keep a travel log to distinguish between private and business trips. An electronic travel log is connected to the car and records all journeys automatically.
What does the Tax Agency say?
A travel log is particularly important in cases like:
1. you use the car mainly for business but some for private use
If you want to avoid being taxed on car benefits, you must be able to show that you have used the employer’s car privately on no more than 10 occasions per calendar year and with a total mileage of no more than 100 mil. Both conditions must be met.
Travel to and from work is considered private trip.
Legal guidance: Evidence issues regarding company car benefits
2. you drive 3000 mil or more on business in an income year
If during an income year you drive more than 3,000 miles in your company car (extensive business driving), your employer can reduce your benefit value by 25%.
If the employer has not reduced the benefit value, you can reduce it yourself in your income tax return if you meet the conditions. An accurate travel log is a good way for you to show how much you have driven on duty.
If you have several employers during the year, you can add up all the mileage you have with the different employers during the year.
3. You have free fuel for your company car.
If your employer pays for the fuel for your company car, you will be taxed on the fuel benefit for the fuel used for your private travel. This requires documentation, such as a driving record, showing how much you have driven the car privately. If there is no good evidence, you will be taxed on all fuel.
4. Employee benefits from congestion tax/infrastructure charge
If your employer pays congestion tax/infrastructure charge for your private trips with your company car, this is a taxable benefit. To calculate the benefit, the employer can use your driving record and the Swedish Transport Agency’s decision.
More information on how the employer calculates the congestion tax / infrastructure charge benefit
What should a travel log contain?
A travel log shall contain:
- meter reading at the beginning of the year
- meter reading at the end of the year.
In addition, the driving record should also contain the following information:
- car registration number
- current year
- date and meter reading at the start and end of the trip
- how many kilometers the employee drives each trip
- which address the journey started from and ended at
- mission/purpose of the trip
- which places, companies or contacts the employee has visited (not necessary for private trips).
- notes on drivers, refueling, etc.
It is a good idea to make a note of the number of liters of fuel and the price when filling up the car. This makes it easier to calculate the value of private driving.
How do you connect the travel log?
The device is easy to install yourself, either directly on the battery or via a plug-in in the vehicle’s OBDII port.
The travel log is housed in a solid and waterproof box (IP65) that ensures it is protected from the environment.
See also our PDF“Installation manual for driving logs“.
How do I add my vehicles to the travel log?
See our manuals
What is temperature monitoring?
The main purpose of temperature monitoring is to ensure that transports of temperature-sensitive goods comply with Swedish legislation, which states that “all spaces for the transport of food are defined as food establishments. These must meet the requirements set out in Regulation (EC) No. 37/2005, (EC) No. 852/2004, (EC) No. 853/2004.”
What are the requirements for air temperature control?
The requirements for instruments (both gauges and sensors) used to measure and record the product temperature of frozen foods are regulated.
for official controls under EC Directive 92/2/EEC and LIVSFS 2006:12. This industry guideline recommends that the same requirements apply to all types of product temperature checks. Similarly, the requirements for instruments used to measure and record air temperature in rooms for the storage and transport of chilled and frozen food are regulated under EC Regulation 37/2005. Table 5 specifies the requirements for each measuring device. For chilled foods there is no layer reference, but the industry guideline sets the same requirements for chilled foods.
It is appropriate to equip permanently installed measuring equipment with alarms for monitoring deviations from the set air temperature. If there is an alarm function available, instructions regarding actions to be taken in case of an alarm should also be provided.
What does Svensk Dagligvaruhandel say?
Each companyt is responsible for ensuring that a self-monitoring program is in place to ensure that the equipment used meets the requirements for conducting food approved/registered activities and that the equipment is fully functional.
This requirement applies regardless of the part of the supply chain in which the equipment is used.
How does temperature monitoring work during transport?
With wireless temperature monitoring from GSGroup, you always have full control of the temperature. Thanks to our wireless temperature sensors, you can measure the temperature at multiple locations within the cargo.
This is because we know that the temperature can vary significantly depending on where in the cargo hold you measure. Each temperature sensor detects the temperature in real time and you can view the temperature on your app or computer at any time. To ensure the temperature throughout the journey, temperature limits are set for each sensor, and should the limit be exceeded, the driver is immediately alerted via an app. This allows the driver to investigate why the temperature has deviated as quickly as possible.
How can I prove that the cold chain has been unbroken throughout the transportation?
Once the transport is completed, the end customer can receive a temperature report for the entire journey. This is to prove that nothing in the load could have been adversely affected due to this. too high or too low a temperature. This is to demonstrate to the end customer that nothing in the load may have been adversely affected by this. too high or too low a temperature.
This is also a safeguard for the transport company if it turns out that parts of the cargo have gone bad due to a defect. incorrect temperature conditions. The transport company can then prove that this did not happen during the transport and avoid possible damages. In conclusion, proper temperature monitoring can reduce the risk of high economic costs.
Who is responsible for control and documentation?
Each time the product passes from one stage to another in the logistics chain, the recipient must carry out checks on the product temperature. The check is carried out by measuring the temperature with a thermometer. The carrier is always responsible for checking the air temperature in the vehicle’s load compartment. Each party is responsible for documenting its part.
|
Steps in the distribution flow |
Responsibility for checking that the product temperature complies with applicable legislation and contractual conditions |
Responsibility for checking that the air temperature complies with the applicable contractual conditions
|
|
Setup at the unloading area |
Outgoing goods handler |
Outgoing goods handler |
|
Loading of vehicles |
Driver |
Driver |
|
Loading of a vehicle, container or trailer to be driven by someone else (e.g. train or boat transport). |
Goods handler of dispatch |
On loading, the dispatching goods handler |
|
Transportation by sealed container or trailer |
Goods handler of dispatch |
On loading, the dispatching goods handler |
|
Transportation by a vehicle loaded by someone other than the driver of the vehicle. |
Dispatching goods handler/driver |
On loading, the dispatching goods handler |
|
Discharge |
Receiving goods handler |
Driver alt. receiving goods handler |
Air temperature requirements during transportation
The air temperature during transport must always be low enough to ensure that quality and food safety are not compromised. For frozen and chilled foods, this means that the selected air temperature should ensure that the product temperature does not fall outside the legal regulations and that the product temperature requirements specified on the product are met. This must be documented e.g. through documented analyses and assessments carried out by persons with relevant competence, s.k. HACCP risk analysis. If an increase in air temperature that affects the product temperature is allowed, this must be taken into account in the sustainability labeling of the products.
Vegetables are often divided into two groups, those that require low temperature.
(cold crops) and those that can be handled at higher temperatures (hot crops) during short-term co-storage and co-loading during transportation. The breakdown is related to the temperature sensitivity of the products.
Note that vegetables are very sensitive to temperature variations and drafts, which have a significant impact on product quality.
What to do in case of co-loading during transport
Co-loading requires an air temperature that ensures that the product temperature of the different products being co-loaded is within legal requirements, that producers’ product temperature requirements are taken into account for products whose temperature is not regulated by law, and that product quality is not impaired.
For frozen products, the regulatory requirement is -18°C or lower in all parts of the product during distribution, storage, handling and transportation. Short-term temperature increases to a maximum of -15°C are acceptable for transportation and local distribution. However, this does not apply to ice cream and ice cream products where -18°C also applies in these situations.
For food of animal origin, specific temperature requirements apply. The product temperature must be maintained during all storage and transportation, up to the retail, restaurant/household and e-commerce consumer.
Checking product temperature at unloading?
When unloading, the refrigeration unit must always be switched off when the cabinet doors are opened (otherwise the outside air will fill the cabinet). Control of product temperature should be included as an instruction in the company’s self-monitoring program.
The first temperature check of the consignment shall be carried out immediately after unloading to give a quick indication. Further measurements shall be made in the hold or directly on the quay of the recipient. The number of measurements is determined by the receiving handler.
Routine control of the product temperature should primarily be carried out as an indicative non-destructive measurement. If the measurement is questioned, a new measurement with another instrument of the same type shall be carried out. In case of different measurement results, the average of the measurements made with the same thermometers applies.
In the event of deviations from statutory or agreed product temperatures or when there are different opinions about the measurement results and if the measurements may form the basis for a return shipment and/or complaint, a destructive measurement (i.e. measurement inside the product) shall always be carried out.
Since there is no regulation of liability for deviations in the delivery to the e-commerce consumer, it is recommended that the respective product owner regulates this via internal complaint procedures. However, the temperature must always be ensured when the goods are handed over to the e-commerce consumer by the party carrying out the transport or the owner of the goods. The definition of liability at handover and complaint procedures are specified in the contract between the owner of the goods and the carrier.
Procedures for temperature anomalies and complaints
Temperature deviation means that the product temperature is higher or lower than the legal, recommended or agreed temperature for the specific product. The tolerance of the temperature measurement is the same as the accuracy of the measuring equipment, i.e.. ±0,5°C.
When returning and complaining about a product due to incorrect product temperature, it is a legal requirement for frozen foods to be able to follow the product’s handling and temperature history back in the chain. This means that all documentation on air and product temperatures should be available. The same principle applies to chilled foods.
Responsibilities and actions in case of established temperature anomaly
The table below describes the responsibilities and actions in case of established temperature deviation related to loading and unloading and unloading at unmanned reception. Unless otherwise agreed by the parties and unless these sectoral guidelines are referred to in the agreement, the matrix applies. Agreements between the parties should describe how any temperature deviations are handled and corrected and who is responsible for taking action. Stakeholders always have the responsibility to save goods if there is a possibility.
It should be regulated in agreements between the client and the service provider how temperature deviations on goods delivered to unmanned stores/restaurants/catering establishments and when e-commerce consumers cannot be present should be handled and who is responsible for measures.
|
Temperature deviation determined during pre-loading inspection |
Activity |
Responsible for carrying out the activity |
|
Determine the extent of the deviation. |
Take enough measurements of the whole consignment to be able to assess its extent. |
Driver & dispatching goods handler |
|
Documentation of the extent of the deviation. |
The dispatching goods handler approves the deviation and its scope. |
Driver & dispatching goods handler |
|
Decision on loading. |
Contact client/carrier for decision/action. |
Driver |
|
Decision on possible loading if the principal/carrier is not available. |
Risk assessment is carried out and decisions on possible loading are made based on the results of temperature checks. Goods owners are informed of the decision. |
Driver |
Maintained and developed by the Council for the Refrigerated and Frozen Food Chain in Sweden version 2.1 2021
International guidelines
The transport of temperature-sensitive goods is highly regulated by the EU. The latest regulation states that
1.1 Commission Directive 92/1/EEC of 13 January 1992 on the monitoring of temperatures in the compartments of transport vehicles, cold stores and freezers containing quick-frozen foodstuffs lays down requirements to ensure compliance with the temperatures laid down in Directive 89/108/EEC.
2.1. Premises for the transport, holding and storage of quick-frozen foodstuffs must be fitted with appropriate measuring instruments to measure and record the air temperature of the quick-frozen foodstuffs at short and regular intervals.
2.2. From January 1, 2006, all instruments used to measure and record temperatures in accordance with paragraph 1 above shall comply with standards EN 12830, EN 13485 and EN 13486. Food business operators shall keep available all documents necessary to verify the conformity of such instruments mentioned above with the applicable EN standard.
However, measuring instruments installed before 31 December 2005 and in accordance with the legislation in force before the adoption of this Regulation may be used until 31 December 2009.
2.3. Temperature records shall be dated and kept by the food business operator for at least one year, or longer if necessary due to the nature and shelf life of the frozen food[2].
The requirements may differ from one type of cargo to another, but there are common guidelines and documentation requirements.
Evidence in a dispute
he contract between the parties should describe how any temperature deviations are handled and corrected, and who is responsible for taking action. Stakeholders always have the responsibility to save goods if there is a possibility. In order for the carrier to be able to disclaim liability and possible claims for compensation, the carrier must be able to prove that the temperature was stable during transportation. Otherwise, the driver is liable unless otherwise agreed, see table below.
| Temperature anomaly detected during pre-loading inspection | Activity | Person responsible |
|
Determine the extent of the deviation. |
Carry out enough measurements on the whole consignment to be able to assess the scope. | Driver & dispatching goods handler |
| Documentation of the extent of the deviation. | The dispatching goods handler approves the deviation and its scope. Measured temperatures and number of damaged carriers are documented on the consignment note and signed. | Driver & dispatching goods handler |
| Decision on loading. | Contact client/carrier for decision/action. | Driver |
| Decision on possible loading if the principal/carrier is not available. | Risk assessment is carried out and decisions on possible loading are made based on the results of temperature checks. Goods owners are informed of the decision. | Driver |
Source: Storage-and-transportation-of-frozen-and-chilled-food.pdf
How can I prove that the cold chain has been unbroken throughout the transportation?
Once the transport is completed, the end customer can receive a temperature report for the entire journey. This is to prove that nothing in the load could have been adversely affected due to this. too high or too low a temperature. This is to demonstrate to the end customer that nothing in the load may have been adversely affected by this. too high or too low a temperature.
This is also a safeguard for the transport company if it turns out that parts of the cargo have gone bad due to a defect. incorrect temperature conditions. The transport company can then prove that this did not happen during the transport and avoid possible damages. In conclusion, proper temperature monitoring can reduce the risk of high economic costs.
To provide you with the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. If you consent to these technologies, we may process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this website. If you do not give your consent or withdraw your consent, it may negatively affect certain functions and features.



